S&P 500 Companies’ Sustainability Reporting and Assurance Practices
In today’s rapidly evolving corporate reporting landscape, investors expect more information from public companies, and many audit committees are taking on additional oversight responsibilities to meet evolving needs and expectations.
At the Center for Audit Quality (CAQ), we know that public company auditors are uniquely positioned to support this shift. Independent assurance from auditors provides valuable information to investors and audit committees as they navigate new challenges by enhancing the reliability and credibility of corporate disclosures.
Every year, we examine sustainability reporting trends among S&P 500 companies to understand how public companies are responding to investor demand and the role that auditors play in supporting these disclosures. Read on for key takeaways from our latest S&P 500 Sustainability Reporting and Assurance Analysis.
Independent assurance from auditors provides valuable information to investors and audit committees as they navigate new challenges by enhancing the reliability and credibility of corporate disclosures.
Use of Sustainability Reporting Standards and Frameworks
We compiled our analysis from company sustainability reports, company websites, completed CDP Climate Change Questionnaires, and third-party assurance or verification reports for 2023 data and found that 99% of S&P 500 companies reported some kind of sustainability-related information during this time, up from 98% in 2022.
Companies continued to mostly use or reference the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) Standards, the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) Recommendations and the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards in their reporting. The majority of companies (over 300 of them) continued to reference all three of those standards or frameworks to help construct their reporting.
Ninety-three companies mentioned the IFRS® Sustainability Disclosure Standards in their sustainability reporting in some way, an increase from the 17 companies that mentioned it in 2022. Many of the companies simply noted that the International Sustainability Standards Board had assumed oversight of the SASB Standards and the TCFD Framework which the companies had used to perform their reporting, and others suggested that they planned to use the IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards in the future.
Companies also mentioned the European Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), the California Climate Laws and the Task Force on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) Recommendations, generally indicating their current or planned future compliance with the relevant requirements or frameworks.
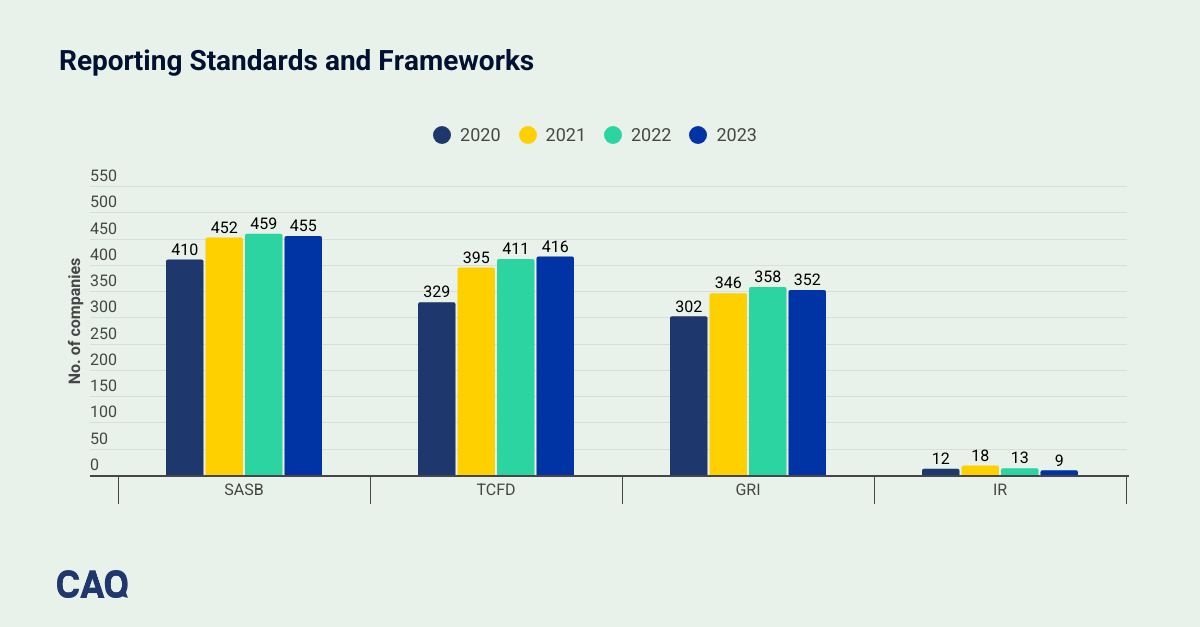
The majority of companies continued to reference all three of those standards or frameworks to help construct their reporting.
Increased Assurance from Auditors
In 2023, 362 companies who reported sustainability information obtained assurance or verification over certain metrics, up 6.5% from 340 companies in 2022. We also saw an upward trend in the companies that obtained assurance from public company auditors – 87 in 2023 compared to 74 in 2022 – an encouraging sign that more public companies recognize the unique value of auditor assurance.
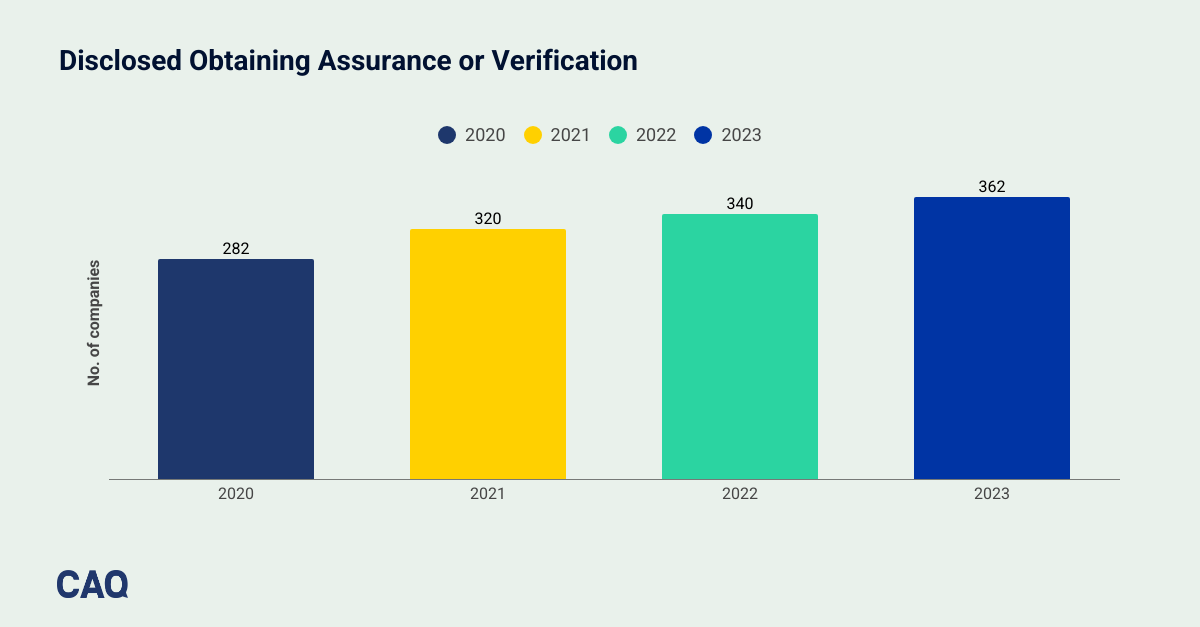
Public company auditors’ tried-and-true approach to assurance enhances stakeholder trust and confidence in management’s data, disclosures, and performance claims, especially in emerging non-financial reporting areas like sustainability. Public company auditors comply with rigorous requirements for independence, firm systems of quality control, and subject matter competency, and they play a critical role in serving the public interest and supporting the flow of reliable information for decision-making.
Of the companies that obtained assurance, 24% obtained assurance from public company auditors. S&P 500 companies continued to increase the scope of information subject to auditor assurance, with the majority obtaining assurance over GHG emissions and 1-3 other sustainability metrics (e.g., water, energy, or waste metrics). Companies also continued to mostly opt for limited assurance engagements over reasonable assurance engagements.
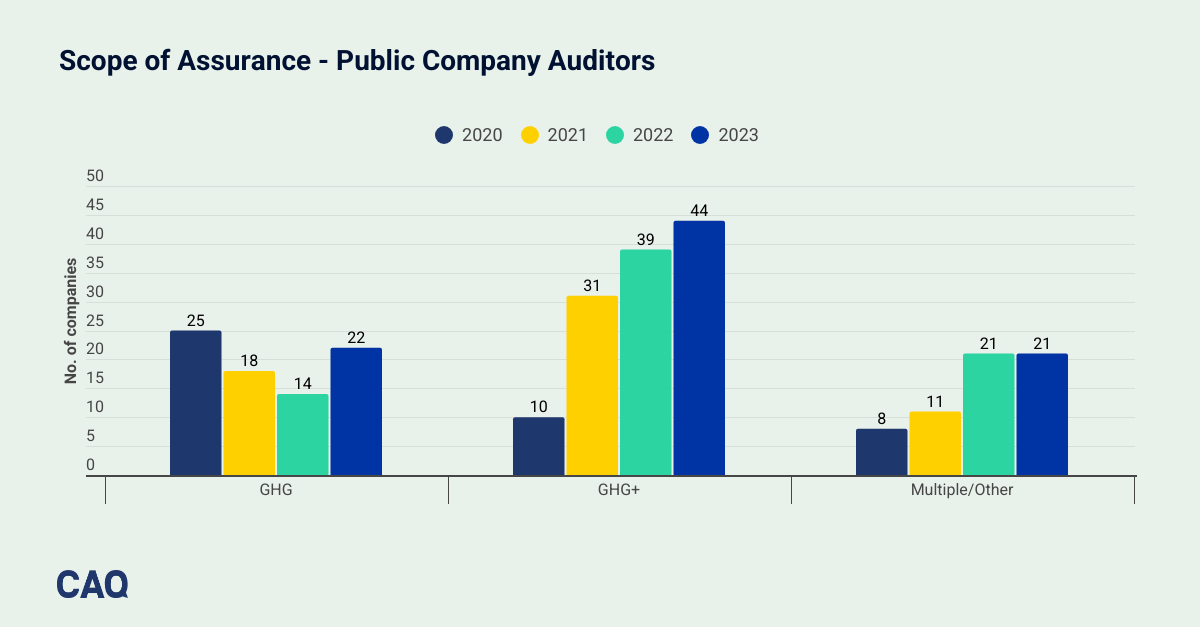
S&P 500 companies continued to increase the scope of information subject to auditor assurance.
GHG Emissions Assurance or Verification
We found that 360 of the 362 companies who obtained some kind of assurance or verification obtained assurance over their GHG emissions. This is an increase of 23 companies compared to 2022.
Companies continued to increase the extent to which they reported and assured the different categories of scope 3 GHG emissions. (All categories besides ‘category 14 – franchises’ experienced increases). The most reported and assured categories of scope 3 GHG emissions continued to be: business travel, purchased goods and services, and fuel and energy related activities with more than 340 companies reporting these categories and over 180 companies obtaining assurance over them.
In addition to GHG emissions, S&P 500 companies obtained assurance over a variety of other topics including water, energy, waste, employee health and safety, and human capital information.
Companies continued to increase the extent to which they reported and assured the different categories of scope 3 GHG emissions.
Disclosures of Net-Zero or Carbon Neutral Commitments
The number of companies who disclosed a net-zero or carbon neutral commitment in 2023 remained relatively consistent with 2022, with only a 4 company increase. Although commitment dates varied for both net-zero and carbon neutral commitments, the most common year noted was 2050.
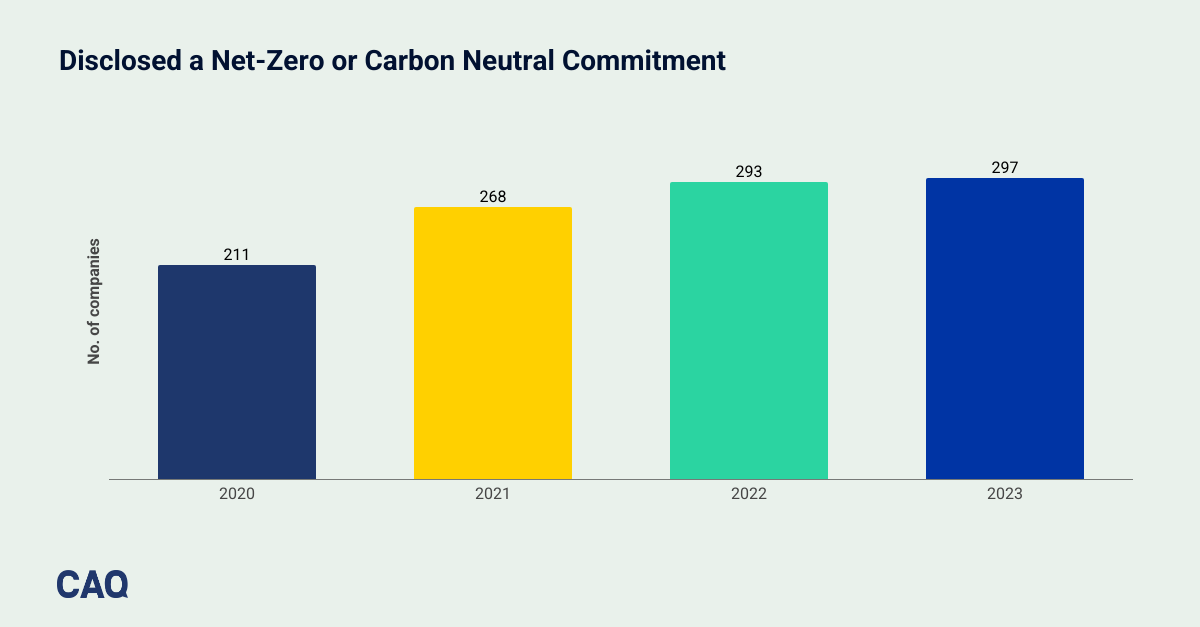
This analysis reaffirms that sustainability data remains an important feature of our corporate reporting landscape for investors, and assurance from public company auditors can enhance trust and confidence in this information. Explore the full S&P 500 analysis here.
